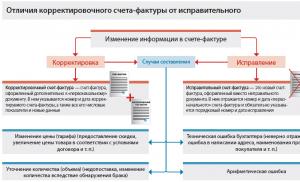
The main stages of a modern lesson. Approximate structure of each type of lesson on the Federal State Educational Standards Stages of a lesson on the Federal State Educational Standards in a primary school
STRUCTURE OF A LESSON ACCORDING TO GEF
1.Structure of a lesson in mastering new knowledge
1) Organizational stage
3) Updating knowledge
4) Primary assimilation of new knowledge
6) Primary consolidation
2. Structure of a lesson on the integrated application of knowledge and skills (consolidation lesson)
1) Organizational stage
2) Checking homework, reproducing and correcting students’ basic knowledge. Updating knowledge
4) Primary consolidation
3. Lesson structure for updating knowledge and skills
(repetition lesson)
1) Organizational stage
2) Checking homework, reproducing and correcting students’ knowledge, skills and abilities necessary for creative solution of assigned problems
3) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities
4) Updating knowledge
7) Control of assimilation, discussion of mistakes made and their correction
1) Organizational stage
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities
3) Updating knowledge
Reproduction at a new level (reworded questions)
5) Application of knowledge and skills in a new situation
7) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
5. Structure of a lesson for monitoring knowledge and skills
1) Organizational stage
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities
3) Identification of knowledge, skills and abilities, checking the level of development of students’ general educational skills. (Tasks in terms of volume or degree of difficulty must correspond to the program and be feasible for each student)
6. Structure of a lesson for correcting knowledge, skills and abilities
1) Organizational stage
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities
3) Results of diagnostics (monitoring) of knowledge, skills and abilities. Identification of typical errors and gaps in knowledge and skills, ways to eliminate them and improve knowledge and skills
Depending on the diagnostic results, the teacher plans collective, group and individual teaching methods
7. Structure of a combined lesson
1) Organizational stage.
3) Updating knowledge.
5) Initial check of understanding
6) Primary consolidation
8) Information about homework, instructions on its implementation
9) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
TYPES OF LESSONS
Lesson type
Purpose
Learning Effectiveness
Lesson on initial presentation of new knowledge
Primary assimilation of new subject and meta-subject knowledge
Reproducing rules, concepts, algorithms in your own words, performing actions according to a model or algorithm
Lesson in the formation of initial subject skills, mastery of subject skills
Application of acquired subject knowledge or methods of educational actions in the context of solving educational problems (tasks)
Correct reproduction of samples of assignments, error-free application of algorithms and rules when solving educational problems
Lesson on the application of meta-subject and subject knowledge
Application of universal educational actions in the context of solving educational problems increased complexity
Independent solution of problems (exercises) of increased complexity by individual students or the class team
Lesson on generalization and systematization of subject knowledge
Systematization of subject knowledge, universal educational activities (solving subject problems)
Ability to formulate a generalized conclusion, level of development of the UUD
Subject knowledge review lesson
Consolidation of subject knowledge, formation of UUD
Error-free execution of exercises, problem solving by individual students and the class team; error-free oral responses; ability to find and correct errors, provide mutual assistance
Test lesson
Testing subject knowledge and skills to solve practical problems
Results of test or independent work
Corrective lesson
Individual work on mistakes made
Independently finding and correcting errors
Integrated lesson
Integration of knowledge about a specific object of study obtained through different means
Deepening knowledge of lesson material through the implementation of interdisciplinary knowledge
Combined lesson
Solving problems that cannot be completed in one lesson
Planned result
SELF-ANALYSIS OF A LESSON ON GEF (1 OPTION)
What is the place of this lesson in the topic?
How is this lesson related to the previous one, and how does it work for subsequent lessons?
What are the purpose and objectives of the lesson (educational, educational, developmental)?
What result did you want to get by the end of the lesson?
How well was the lesson content selected in accordance with the intended purpose?
Was time allocated rationally between the stages of the lesson?
Were the “connections” between the stages of the lesson logical?
What role did visual aids play in achieving your goal?
How successfully was the quality of knowledge, skills and corrections monitored during the lesson?
Are the volume and content of homework correctly determined, taking into account the purpose, characteristics of the class and the quality of learning the material in the lesson?
Psychological atmosphere of the lesson.
Did the students get satisfaction from the lesson?
How do you yourself evaluate the results of your lesson?
Did you manage to achieve all the objectives of the lesson?
If it failed, then why?
Did you get satisfaction from the lesson?
What needs to be fixed?
What else needs to be worked on?
SELF-ANALYSIS OF A LESSON ON GEF (OPTION 2)
Today's lesson... (No.) in the system of lessons on the topic (section)....
Its goal is ..., I included ... among the educational objectives of the lesson, and ... among the educational objectives, the lesson was also designed to promote the development of students ....
In this class..., so I....
This is a type of... lesson, it included... stages:.... The main stage was ..., the tasks of the ... stage were ..., and the ... stage was ....
When conducting the lesson, I was guided by the principles of teaching: ....
To solve the purpose of the lesson, I selected... (content: examples, questions, assignment).
The lesson material turned out to be... (difficult, easy, interesting for students).
At the ... stage of the lesson, I used ... (what?) teaching methods, because .... At the stage... -... (what?) methods.
During the lesson at the ... stage ... (individual, frontal, group, collective) was organized, and at the ... stage ... the work of students, because ....
The tasks... were focused on the development... of students.
The teacher’s guidance when performing ... tasks was ... (operational, instructive), because ....
Students had the opportunity to choose...
I (failed) to meet the deadline. The time distribution was…. The pace of the lesson….
It was... (easy...) for me to teach the lesson, the students... got involved in the work.... I was pleased..., surprised..., saddened... (which of the students?), because....
Notes on the board... Visual material (other teaching aids)….
Homework (will not) cause difficulties for ... students because
USEFUL LINKS FOR TEACHERS
Methodological Council (teacher's methodological portal)metodsovet.moy.su/
Head teacher info www.zavuch.info/
Primary school teacher websitesuchportal.ru/dir/5-2-2
Creative Teachers Networkit-n.ru/
Primary school. /www.nachalka.com/
Primary school management.www.pervoklassnik.resobr.ru/
Early Childhood Developmentwww.danilova.ru/
September 1 (advice to parents and students).www.1sentyabrya.ru/
Holiday scenarios.www.teacherday.narod.ru/
Free lesson development, scripts, testing, karaoke tunes, etc.http://www. uroki. net./
Sun. http://www. solnet. ee/index. html
LenaGold. Collection of backgrounds and cliparts.http://lenagold.ru/
Festival of pedagogical ideas. Open lesson.http://festival.1september.ru/
Portal for teachers “To help the modern teacher.”http://k-yroky.ru/
Publishing house "1 September". Newspapers and magazines by subject.http://www.1september.ru/
A unified collection of digital educational resources.http://school-collection.edu.ru/
Pedagogical community (pedagogical council)http://pedsovet.su/
Collection of RusEdu presentationshttp://www.rusedu.ru/
Methodists. Professional community of teachers.http://metodisty.ru/index.php
Presentation collectionhttp://www.ppt.3dn.ru/
Country of Mastershttp://stranamasterov.ru/
Head teacher http://www.zavuch.info/
Open classhttp://www.opencl ass.ru/
The best children's sites on narod.ruhttp://nashidetochki.narod.ru/
Red Book of Russiahttp://www.biodat.ru/db/rb/index.htm
International Red Bookhttp://www.floranimal.ru/intredbook.php
Teacher portalhttp://www.uchportal.ru/
Librarian (electronic library)http://bibliotekar.ru/
International Union of Educational Sites (Web Circle of Friends)http://webkolo.clan.su/
Educational portal OUTSIDE CLASShttp://vneuroka.ru/
Approximate structure of each type of lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard
1. Structure of a lesson in mastering new knowledge:
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Updating knowledge.
4) Primary assimilation of new knowledge.
5) Initial check of understanding
6) Primary consolidation.
7) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
8) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
2 The structure of a lesson on the integrated application of knowledge and skills (a lesson on consolidation) .
1) Organizational stage.
2) Checking homework, reproducing and correcting students’ basic knowledge. Updating knowledge.
4) Primary consolidation
in a familiar situation (typical)
in a changed situation (constructive)
5) Creative application and acquisition of knowledge in a new situation (problem tasks)
6) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
7) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
3. Structure of a lesson on updating knowledge and skills (repetition lesson)
1) Organizational stage.
2) Checking homework, reproducing and correcting the knowledge, skills and abilities of students necessary for creative solution of assigned problems.
3) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
4) Updating knowledge.
in order to prepare for the test lesson
in order to prepare for studying a new topic
5) Application of knowledge and skills in a new situation
6) Generalization and systematization of knowledge
7) Control of assimilation, discussion of mistakes made and their correction.
8) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
9) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
4. Lesson structure of systematization and generalization of knowledge and skills
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Updating knowledge.
4) Generalization and systematization of knowledge
Preparing students for general activities
Reproduction at a new level (reformulated questions).
5) Application of knowledge and skills in a new situation
6) Monitoring learning, discussing mistakes made and correcting them.
7) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
Analysis and content of the work results, drawing conclusions based on the studied material
5. Structure of a lesson on testing knowledge and skills
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Identification of knowledge, skills and abilities, checking the level of development of students’ general educational skills. (Tasks in volume or degree of difficulty must correspond to the program and be feasible for each student).
Control lessons can be written control lessons, lessons combining oral and written control. Depending on the type of control, its final structure is formed
4) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
6. Structure of a lesson for correcting knowledge, skills and abilities.
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Results of diagnostics (monitoring) of knowledge, skills and abilities. Identification of typical errors and gaps in knowledge and skills, ways to eliminate them and improve knowledge and skills.
Depending on the diagnostic results, the teacher plans collective, group and individual teaching methods.
4) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
5) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
7. Structure of a combined lesson.
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Updating knowledge.
4) Primary assimilation of new knowledge.
5) Initial check of understanding
6) Primary consolidation
7) Control of assimilation, discussion of mistakes made and their correction.
8) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
9) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
ONZ lesson structure.
1. Motivation (self-determination) for educational activities (“need” - “want” - “can”) 1-2 min.
2. Updating and recording individual difficulties in a trial educational action – 5-6 minutes.
3. Identifying the location and cause of the difficulty – 2-3 minutes.
4. Construction of a project for getting out of a difficulty – 5-6 min.
5. Implementation of the constructed project - 5-6 minutes.
6. Primary consolidation with pronunciation in external speech – 4-5 minutes.
7. Independent work with self-test using a standard – 4-5 minutes.
8. Inclusion in the knowledge system and repetition – 4-5 min.
9. Reflection on educational activities – 2-3 min.
Students' ability to learn:
1-4 min. – 60% information
5 - 23 min. – 80% of information
24 -34 min. – 50% information
35 -45 min. – 6% information
How to build a lesson to implement the requirementsSecond generation standards?
To construct a lesson within the framework of the Federal State Educational Standard of Education, it is important to understand what the criteria for the effectiveness of the lesson should be.
1. Lesson goals are set with a tendency to transfer functions from teacher to student.
2. The teacher systematically teaches children to carry out reflexive action (assess their readiness, detect ignorance, find the causes of difficulties, etc.)
3. A variety of forms, methods and techniques of teaching are used to increase the degree of student activity in the educational process.
4. The teacher knows the technology of dialogue, teaches students to pose and address questions.
5. The teacher effectively (adequate to the purpose of the lesson) combines reproductive and problem-based forms of education, teaches children to work according to the rule and creatively.
6. During the lesson, tasks and clear criteria for self-control and self-assessment are set (there is a special formation of control and evaluation activities among students).
7. The teacher achieves comprehension educational material by all students, using special techniques for this.
8. The teacher strives to evaluate the actual progress of each student, encourages and supports minimal success.
9. The teacher specifically plans the communicative tasks of the lesson.
10. The teacher accepts and encourages the student’s own position, a different opinion, and teaches the correct forms of their expression.
11. The style and tone of relationships set in the lesson create an atmosphere of cooperation, co-creation, and psychological comfort.
12. In the lesson there is a deep personal impact “teacher - student” (through relationships, joint activities, etc.)
Let's consider the approximate structure of a lesson introducing new knowledge within the framework of the activity approach.
1. Motivation for educational activities. This stage of the learning process involves the student’s conscious entry into the space of learning activity in the lesson.
For this purpose, at this stage, his motivation for educational activities is organized, namely: 1) the requirements for him from educational activities are updated (“must”);
2) conditions are created for the emergence of an internal need for inclusion in educational activities (“I want”);
3) a thematic framework is established (“I can”). In the developed version, processes of adequate self-determination in educational activities and self-reliance in it occur here, implying the student’s comparison of his real “I” with the image “I am an ideal student,” conscious subordination of oneself to a system of normative requirements educational activities and the development of internal readiness for their implementation.
2. Updating and recording individual difficulties in a trial educational action. At this stage, preparation and motivation of students for proper independent implementation trial educational action, its implementation and recording of individual difficulties. Accordingly, this stage involves:
1) updating the studied methods of action sufficient to construct new knowledge, their generalization and symbolic fixation;
2) updating of relevant mental operations and cognitive processes;
3) motivation for a trial educational action (“need” - “can” - “want”) and its independent implementation;
4) recording individual difficulties in performing a trial educational action or justifying it. 3. Identifying the location and cause of the difficulty. At this stage, the teacher organizes for students to identify the location and cause of the difficulty. To do this, students must:
1) restore the operations performed and record (verbally and symbolically) the place - step, operation where the difficulty arose;
2) correlate your actions with the method of action used (algorithm, concept, etc.) and on this basis, identify and record in external speech the cause of the difficulty - those specific knowledge, skills or abilities that are lacking to solve the original problem and problems of this class or like in general
4. Construction of a project for getting out of the difficulty (goal and topic, method, plan, means). At this stage, students in a communicative form think about the project of future educational actions: they set a goal (the goal is always to eliminate the difficulty that has arisen), agree on the topic of the lesson, choose a method, build a plan to achieve the goal and determine the means - algorithms, models, etc. This process is led by the teacher: at first with the help of introductory dialogue, then with stimulating dialogue, and then with the help of research methods.
5. Implementation of the constructed project. At this stage, the completed project is being implemented: various options proposed by students are discussed and a choice is made. best option, which is fixed in language verbally and symbolically. The constructed method of action is used to solve the original problem that caused the difficulty. At the end, the general nature of the new knowledge is clarified and the overcoming of the previously encountered difficulty is recorded.
6. Primary consolidation with pronunciation in external speech. At this stage, students, in the form of communication (frontally, in groups, in pairs), solve standard tasks for a new method of action, pronouncing the solution algorithm out loud.
7. Independent work with self-test according to the standard. When carrying out this stage, an individual form of work is used: students independently perform tasks of a new type and self-test them, step by step comparing them with the standard. At the end, a performance reflection on the progress of the implementation of the constructed project of educational actions and control procedures is organized. The emotional focus of the stage is to organize, if possible, a situation of success for each student, motivating him to engage in further cognitive activity.
8. Inclusion in the knowledge system and repetition. At this stage, the boundaries of applicability of new knowledge are identified and tasks are performed in which a new method of action is provided as an intermediate step. When organizing this stage, the teacher selects tasks that train the use of previously studied material that has methodological value for introducing new methods of action in the future. Thus, on the one hand, there is an automation of mental actions according to the learned norms, and on the other, preparation for the introduction of new norms in the future.
9. Reflection on learning activities in the lesson (result). At this stage, new content learned in the lesson is recorded, and reflection and self-assessment of students’ own learning activities is organized. At the end, its goal and results are correlated, the degree of their compliance is recorded, and further goals of the activity are outlined.
What regulatory document regulates public relations in the field of education? Law “On Education in Russian Federation»
The official source of publication of regulatory legal acts of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation is?“Bulletin of normative acts of federal executive authorities” and the corresponding website
Which document enshrines the basic provisions on the rights of the child? International Covenant on Civil Rights
The parties to the employment contract in educational organization are: head of an educational organization and teacher
The Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” establishes the following levels of general education: preschool and primary general education, basic general and secondary general education;
The Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” establishes the following levels of professional education: average vocational education, higher education (bachelor's, specialist's, master's degrees), higher education - training of highly qualified personnel;
Is it possible to receive education in an educational organization in the Russian Federation in the language of other peoples?it is possible to receive preschool, primary and basic general education in the native language from among the peoples of Russia;
Which of the following documents is the administration of an educational organization obliged to familiarize the child and his parents (legal representatives) with upon admission?charter of an educational organization
What is the subject of pedagogy? education as a pedagogical process; 4. development.
Which approach in pedagogy is called axiological? personality orientation
Which component of the educational process is system-forming? goal setting
Which characteristic is most effective for team building? teacher's knowledge of team theory
The leading factor in the development of a person as an individual is: upbringing
In the works of which teacher did the class-lesson form of classes first receive theoretical justification? Ya.A. Comenius
Methods for forming personality consciousness include: competition
Which of the following documents does not regulate the educational process? methodological manual
What is didactics? theory of learning, education and upbringing
The process of assimilating social norms, values, and typical forms of behavior is called: socialization
In the process of pedagogical interaction between the teacher and students, the following relationships develop: subject-object.
Technology education is... a system of scientifically based methods and techniques that contribute to the establishment of such relationships between the teacher and the student, in which the given goal is achieved;
Which approach to educational activities is more conducive to the application of knowledge in practice?Active;
What methods and technologies contribute to the formation of social qualities of students? technology of cooperation and mutual learning;
Assimilation of knowledge and mastery of generalized methods of action is the subject of: 1. joint activity of teacher and student2. educational activities3. pedagogical activity√4. all answers are correct
The educational system is... social institutions that provide training and education of a person
An individual approach to a person as an individual with an understanding of it as a reflecting system that determines all other mental phenomena is the essence:the principle of a person-centered approach
For volitional regulation of behavior and activities, the following actions are necessary: conscious
According to the concept of G. Eysenck, an emotionally unstable introvert is: melancholic
According to I.P. Pavlov’s classification of temperament types must be built taking into account: features of functioning nervous system
Characteristics mental development during a stable period it is considered... absence of disturbances in interpersonal relationships
… that special combination of internal development processes and conditions that are typical for each age stage and determine the dynamics of mental development throughout the corresponding age period and new qualitatively unique psychological formations emerging towards its end.social development situation
Worldview and professional interests are personal new formations.... age. high school
The leading activity of a teenager is: communication with peers
In the theory of cultural and historical development of the psyche L.S. Vygotsky, considering the issue of the relationship between training and development, showed that not all training is effective, but only that which is in the zone... .its immediate development
Who was one of the first in our country to develop the psychological and pedagogical concept of problem-based learning? L.V. Zankov
The subject’s activity in mastering generalized methods of educational actions and self-development in the process of solving educational tasks specifically set by the teacher, on the basis of external control and assessment, turning into self-control and self-assessmenteducational activities
Means nonverbal communication is not: speech
Agreement through mutual concession in the event of a clash of any interests or aspirations: compromise
Comprehension emotional state, penetration, feeling into the experiences of another person is: empathy
The mechanism of social perception, which is based on a person’s ability to imagine how he is perceived by his communication partner, is social...reflection
The Federal State Educational Standard is a document regulating: basic educational programs of primary, basic and general secondary education
The set of views, ideas, ideas aimed at studying and explaining pedagogical phenomena is called:pedagogical theory
Method in pedagogy is... a way to achieve a pedagogical goal and solve educational and training problems
The main organizational form of training is: lesson
For use in educational institution Textbooks allowed: recommended and approved by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
The professional competence of a teacher is: knowledge, experience and a set of professional and personal qualities that provide effective solutions to issues of training and education
The study of educational material, built sequentially, with gradual complication and deepening of knowledge, is defined as:linear way of constructing content
The techniques may be of the following nature: logical, organizational and technical
An innovative type of training, the content of which is structured into autonomous organizational and methodological blocks that make it possible to adapt the educational process to individual capabilities students is defined as:distance learning
Federal state educational standards include requirements for... 1. structure of the main educational programs2. conditions for the implementation of basic educational programs 3. results of mastering basic educational programs√4. all of the above options are correct
Material objects that are carriers educational information and a tool for the activities of the teacher and students, are defined as: teaching aids
Problem-based learning is revealed through: . formulation by the teacher and resolution by the student of a problematic question, task and situation
The term “educational teaching” was introduced by the famous educator I.F. Herbart
Innovations in education are: dissemination of innovations in teaching practice
Motivations that cause human activity and determine its direction motivation
Exposition; Development of action; Climax; Tie; Denouement
Certification tests on the basics of pedagogy and psychology
1 option
1. Parenting techniques - This:
A)part of the general method
B) form of organization of education
C) means of education
D) educational situations
E) optimization criteria
2. Basic method of education
A)belief
B) teacher's word
C) training
D) exercise
E) example
3. General method of formation necessary qualities called :
A) gymnastics
B) education
C) conversation
D) training
E)exercise
4. Logic of education:
A) design, forecast, diagnostics, organization, control, analysis
B) analysis, design, forecast, diagnostics, organization, control
C) analysis, design, forecast, diagnostics, control, organization
D)diagnostics, analysis, forecast, design, organization, control
E) analysis, diagnostics, forecast, design, organization, control
5. The criterion for the effectiveness of education is
A)formation of skills and behavior in accordance with the age of students
B) the contradiction between the environmental requirements for a person and his capabilities
C) formation of aesthetic taste
D) development of artistic taste, improvement of emotional well-being
E) level of professional training
6. Psychological state of difficulty, inability to explain a fact or solve a problem based on existing knowledge:
A) Low level students' knowledge
B)Problem situation
C) Low level of teacher knowledge
D) Difficulties encountered in the educational process
E) Inconsistency of student knowledge with necessary requirements
7. Dialogue as a form, principle, means of teaching, it determines the goals and content of training in technology :
A) L.V. Zankova
B) A.G. Rivina
C) A.A. Amonashvili
D) D.B. Elkonina – V.V. Davydova
E)V.S.Bibler, S.Yu.Kurganova
8. An educational conversation, during which questions are asked primarily by students - eu t:
A) discussion
B) poll
C) discussion
D) dialogue
E)consultation
9. Involving all senses in the perception of educational material is a principle
A) Strength
B) Scientific
C) Systematicity and consistency
D) Availability
E)Visibility
10. The way to achieve the goal and objectives of training:
A) Form of study
B) Teaching Methodology
C)Teaching method
D) Method of teaching
E) Learning principle
11 . Educational programs are developed based on :
A) education concepts
B) educational development programs
C) education law
D) textbooks
E)educational standards
12. Branch of pedagogical science that studies the process of updating pedagogical activities sti:
A) Innovative training
B)Pedagogical innovation
D) Innovative education
13. Steps required to prepare a lesson:
A) forecasting, training, exercises
B) planning, lesson progress, reflection
C)diagnostics, forecasting, planning
D) diagnosis, planning, mastery of implementation
E) forecasting, collecting educational information, mental gymnastics
14. The level of aspirations is characterized by:
A)desired level of personal self-esteem
B) feature volitional sphere individual, expressed in the desire to act in his own way
C) the choice by the subject of the goal of the next action, formed as a result of experiencing the success or failure of a number of past actions
D) a property of the nervous system that expresses the relationship between excitation and inhibition
E) the level of difficulty of future actions
15. Personality structure component
A) thinking
B) age
C) character
D)memory
E) floor
16. Disclosure of the mechanisms and patterns of teaching and educational influence on the intellectual and personal development of the student is the task
A) Pedagogical management
B) Developmental psychology
C)Educational psychology
D) Pedagogy
E) Didactics
17. The system of conditions external to the subject that encourage and mediate his activity is
A) teacher influence
B)pedagogical situation
C) condition of education
D) contract
E) pedagogical significance
18. The main driving force for human development:
A) Genotype
B) Education
C) Learning
D)Education
E) Innate qualities
19. Section educational psychology:
A) psychology of a primary school student
B)psychology of education
C) psychology of a teenager
D) developmental psychology
E) youth psychology
20. The ability to perform certain actions with good quality and successfully cope with activities that include these actions is:
A) Interaction
B) Knowledge
C) Habit
D)Skill
E) Skill
Option 2
1. The idea of the integrity of the educational process is implemented in practice through:
A) cultural approach
B) psychological approach
C) individual approach
D)integrated approach
E) systems approach
2. The principle of parallel influence in collective theory :
A) Cooperation of family, school, community
B) Relationships between teachers and students
C)Influence on the student through the team
D) The influence of parents and educators on the student
E) Influence on the will, consciousness and behavior of the pupil
3. Punishment:
A) Requests, incentives, good deeds
B) Method of education, manifested in the form of demands
C) Managing student activities through a variety of repetitive tasks
D)A method of influencing a student in order to stop his negative actions
E) Impact on students’ knowledge in order to clarify the facts and phenomena of life
4. Educational process – process:
A) interactions
B)impact
C) reflection
D) reverse action
E) actions
5. The main signs of the effectiveness of the education process are:
A) knowledge, skills and abilities
B) individual characteristics of the student
C) academic performance
D) adaptation to conditions
E)student behavior
6. Consideration of pedagogical technologies as part of pedagogical science according to this corresponds to……….. aspect of their analysis
A) Private scientific
B) Particularly descriptive
C) Procedural-descriptive
D) Descriptive-effective
E)Scientific
7. The stage of consolidating knowledge and developing skills in the lesson involves
A) Educational reflection and assessment of the quality of work in the lesson
B) Systematization, generalization, reproduction of educational material by topic and section
C) Presentation of educational material with the active involvement of students
D) Determining the degree of assimilation of the studied educational material
E)Development of skills and abilities to apply knowledge
8. Visual teaching methods can be divided into two groups:
A)Illustration and demonstration
B) Talk and demonstration
C) Workshop and observation
D) Verbal and visual
E) Discussion and video method
9. The type of cognitive activity serves as the basis for classification:
A) Inductive and deductive
B) Information-reporting, explanatory, instructive-practical, stimulating method
C)Explanatory and illustrative, reproductive, problem presentation, partial search and research methods
D) Verbal, visual and practical methods
E) Organization of educational and cognitive activities, stimulation and motivation, methods of control and self-control
10. Teaching method:
A) The method of coordinated activity between teacher and student, carried out in in the prescribed manner and a certain mode
B) Fundamental requirement for the practical organization of the educational process
C)A method of joint activity between teachers and students aimed at solving learning problems
D) Managing the process of transition from theory to practice in the learning process
E) Determination of the effectiveness of training in unity with the conditions for its implementation
11. Sequence of stages of the assimilation process:
A) acquisition of knowledge – memorization – application in practice
B) statement of the problem - putting forward a hypothesis - proving it
C) sensation – perception – awareness
D)perception – comprehension – consolidation – application
E) remembering – understanding – comprehension – generalization
12. Innovation in pedagogical activity:
A)Pedagogical innovation
B) Innovation activities
C) Innovative education
D) Pedagogical innovation
E) Innovative training
13. The process of obtaining information about the state of the pedagogical process using a set of methods, techniques, methods:
A) Pedagogical monitoring
B)Pedagogical diagnostics
C) Pedagogical reflection
D) Pedagogical management
14. The desire to satisfy selfish personal needs and interests without regard to the needs and interests of others:
A)selfishness
B) altruism
C) socialization
D) despotism
E) centrism
15. The ability of the individual to adapt to all the diversity of life under any conditions:
A) compatibility
B) leadership
C)adaptability
D) plasticity
E) maladjustment
16. A teacher’s abilities that determine high results in any activity :
A) verbal
B)general
C) special
D) non-verbal
E) communicative
17. The attractiveness of educational material, which evokes certain feelings and contributes to the success of learning:
A) meaningfulness of knowledge
B) the importance of learning
C)emotional characteristics
D) difficulty of execution
E) volume of material
18. Transition of external objective actions into internal mental ones:
A)interiorization
B) exteriorization
C) validity
D) activation
E) sublimation
19. Features of family upbringing, position in the community, role attributes, and institutional status are among the causes of difficulties in pedagogical communication:
A)status-positional-role
B) individual psychological
C) interpersonal-social
D) ethno-sociocultural
E) age-individual
20. In accordance with the theory of P.Ya. Galperin, at this stage students perform actions in terms of loud speeches:
A) motivational
B) materialized
C) control
D)external speech
E) approximate
Target: familiarization with the requirements of a modern lesson within the framework of the Federal State Educational Standard.
Tasks: analyze and compare a modern lesson with a lesson in a traditional school.
Expected result: they can
- Distinguish a modern lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard from a traditional lesson - basic level
- Making a technological map for a modern lesson - advanced level.
Progress of the teachers' council
1. Organizational moment.
Emotional mood - slides (methods, techniques, types of lessons, forms of teaching...)
2. Updating basic knowledge
What do all these words have in common? The topic of our teachers' council is “Modern requirements for a lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard”
Assignment (group work) table “ZKHU”. Statements by representatives from groups + additions from other groups.
3. Statement of the problem
The question to which you and I must find the answer is “A modern lesson on the Federal State Educational Standard, its features”
Expected Outcome: What will we learn?
4. Discovery of “new knowledge”
Opening remarks. Modern society needs educated, moral, enterprising people who can:
- analyze your actions;
- make decisions independently, predicting them possible consequences;
- be distinguished by mobility;
- be capable of cooperation;
- have a sense of responsibility for the fate of the country, its socio-economic prosperity.
The fundamental difference of the modern approach is the orientation of standards on the results of mastering basic educational programs. Results mean not only subject knowledge, but also the ability to apply this knowledge in practical activities. Therefore, educational activities are built on the basis of an activity approach, the purpose of which is to develop the student’s personality on the basis of mastering universal methods of activity. A child cannot develop if he passively perceives educational material. It is his own action that can become the basis for the formation of his independence in the future. This means that the educational task is to organize conditions that provoke children's action.
5. Work on a new topic
The Federal State Educational Standard introduces a new concept - an educational situation, which means a special unit of the educational process in which children, with the help of a teacher, discover the subject of their action, explore it, performing various educational actions, transform it, for example, reformulate it, or offer their own description, etc. etc., partially - they remember. In connection with the new requirements, the teacher is tasked with learning to create learning situations as special structural units of educational activity, as well as being able to translate educational tasks into a learning situation.
The creation of a learning situation should take into account:
- child's age;
- specifics of the academic subject;
- measures of the formation of students' UAL.
To create a learning situation, the following techniques can be used:
- present contradictory facts and theories;
- expose everyday ideas and present scientific facts;
- use the “bright spot” and “relevance” techniques.
In this case, the educational material being studied acts as material for creating a learning situation in which the child performs certain actions (works with reference literature, analyzes the text, finds spelling patterns, grouping them or identifying groups among them). Masters the methods of action characteristic of the subject, i.e. acquires, along with subject, cognitive and communicative competencies.
The learning situation is one of the innovations of the modern lesson. What else is new about the modern lesson in the context of the introduction of the second generation standard? Let's take a closer look at the following positions:
- Place in educational process. The lesson has lost its role as the main and only organizational form of education. Its competitors: informational, home and additional education.
- Structure.
Approximate structure of each type of lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard
1. Structure of a lesson in mastering new knowledge:
1) Organizational stage.
3) Updating knowledge.
6) Primary consolidation.
7) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
8) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
2. The structure of a lesson on the integrated application of knowledge and skills (consolidation lesson).
1) Organizational stage.
2) Checking homework, reproducing and correcting students’ basic knowledge. Updating knowledge.
4) Primary consolidation in a familiar situation (typical) in a changed situation (constructive)
5) Creative application and acquisition of knowledge in a new situation (problem tasks)
6) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
3. Structure of a lesson on updating knowledge and skills (repetition lesson)
1) Organizational stage.
2) Checking homework, reproducing and correcting the knowledge, skills and abilities of students necessary for creative solution of assigned problems.
3) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
4) Updating knowledge.
- in order to prepare for the test lesson
- in order to prepare for studying a new topic
6) Generalization and systematization of knowledge
9) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
4. Lesson structure of systematization and generalization of knowledge and skills
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Updating knowledge.
4) Generalization and systematization of knowledge
- Preparing students for general activities
- Reproduction at a new level (reformulated questions).
5) Application of knowledge and skills in a new situation
6) Monitoring learning, discussing mistakes made and correcting them.
7) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
5. Structure of a lesson for monitoring knowledge and skills
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Identification of knowledge, skills and abilities, checking the level of development of students’ general educational skills. (Tasks in volume or degree of difficulty must correspond to the program and be feasible for each student).
Control lessons can be written control lessons, lessons combining oral and written control. Depending on the type of control, its final structure is formed
4) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
6. Structure of a lesson for correcting knowledge, skills and abilities.
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Results of diagnostics (monitoring) of knowledge, skills and abilities. Identification of typical errors and gaps in knowledge and skills, ways to eliminate them and improve knowledge and skills.
Depending on the diagnostic results, the teacher plans collective, group and individual teaching methods.
4) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
5) Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
7. Structure of a combined lesson.
1) Organizational stage.
2) Setting the goals and objectives of the lesson. Motivation for students' learning activities.
3) Updating knowledge.
4) Primary assimilation of new knowledge.
5) Initial check of understanding
6) Primary consolidation
7) Control of assimilation, discussion of mistakes made and their correction.
8) Information about homework, instructions on how to complete it
Reflection (summarizing the lesson)
Non-traditional lesson forms
Organizational forms (individual, group, differentiated group, frontal; academic, leisure, interactive)
Methodology (problem-based, research, project-based learning; developmental, student-centered, reflective learning, productive technologies)
Means
What are the requirements for a modern lesson? :
- a well-organized lesson in a well-equipped classroom should have a good start and a good ending;
- the teacher must plan his activities and the activities of his students, clearly formulate the topic, purpose, and objectives of the lesson;
- the lesson should be problematic and developmental: the teacher himself aims to cooperate with students and knows how to direct students to cooperate with the teacher and classmates;
- the teacher organizes problem and search situations, activates the activities of students;
- the students themselves make the conclusion;
- minimum reproduction and maximum creativity and co-creation;
- saving time and saving health;
- the focus of the lesson is children;
- taking into account the level and capabilities of students, which takes into account such aspects as the profile of the class, the aspirations of students, and the mood of children;
- the ability to demonstrate the methodological art of a teacher;
- planning feedback;
- the lesson should be good.
Independent work with verification + control and self-assessment
Independent completion of a lesson flow chart (group work) with verification
Reflection
- Table “ZHU”,
- Expected result
- Reception of “Unfinished phrases”
8. Completion of the teachers' meeting
A training session is an important part of the educational process, which requires serious preparation from students and teachers. With the introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard, its role, as well as its content and methodological content, have undergone changes. All stages of a lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard carefully designed by the teacher to:
- the teacher created searching and problem situations, stimulating and intensifying the activities of students;
- each stage was fully implemented, the characteristics, age, and character of the children were taken into account;
- the classes were held in the key of freedom of choice of actions, openness and work for maximum results;
- the teacher can adjust and control the course of the educational session to achieve maximum effectiveness;
- the teacher could give children not only knowledge, but also the ability to apply it in various situations, including those that go beyond the scope of the subject being studied (interdisciplinary connections).
Stages of a modern lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard
Lesson on Federal State Educational Standards latest generation- an effective process that is interconnected with the interests of society, school and students. All stages of a lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard are designed on a system-activity approach designed to teach children to learn, motivate them for self-education and self-development, since the state needs a generation of mobile modern people who are able to analyze their actions, bear responsibility for them, predict the situation, and be ready to cooperate.
There are four main groups of training sessions:
- Discovery of new knowledge.
- Developmental control.
- Reflections.
- General methodological orientation.
In accordance with the requirements of the state standard, training sessions must be structured in an individualized and student-oriented manner. The priority is given to the independent work of schoolchildren, rather than the dominance of the teacher. The authoritarian style of presentation is archaic; it is being replaced by partner mutual assistance in mastering new knowledge and skills.
By carefully developing a lesson plan according to the Federal State Educational Standard, the teacher presents the material in a structured, concise and logical sequence, which allows you to determine options and tasks for each lesson. If necessary, the teacher can change the lesson plan during the organizational stage. In primary and secondary schools, everyone stage of a modern lesson on the Federal State Educational Standard in the context of learning new material, it is based on involving children in mental activity, practical tasks, and memorization.
Stages of a lesson on the Federal State Educational Standard in elementary school
According to the second generation federal standard, the course of all stages of the lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard in elementary school should ensure not the transfer of knowledge and skills from the teacher to students, but the development in children of the ability to independently pose an educational problem, search for and formulate a way to solve it (the teacher is assigned the role of assessing the achieved result).
The updated lesson technology assumes that:
- The task of the lesson is the discovery, search and awareness of truth, which occurs during the interaction between the teacher and students.
- The lesson takes place in the context of a universal cultural paradigm.
- A person on the path of understanding the truth is the highest value, the goal, but not the means.
Stages of a lesson on the Federal State Educational Standard in elementary school They are somewhat different from the main class because they have a number of features. All of them are aimed at stimulating children’s self-development, students’ ability to choose goals commensurate with their capabilities, make decisions, look for ways to solve complex and non-standard problems, control their own actions, communicate with other people, seek compromises, coordinate and argue their point of view.
In the context of the Federal State Educational Standard, a modern lesson should transform a primary school student from a passive listener who perceives the information given by the teacher into a researcher who independently obtains knowledge. At the same time, the teacher must be able to reveal the student’s abilities, evaluate his cognitive style in order to stimulate an active student position.
All stages of a lesson on the Federal State Educational Standard in primary link are reduced to stimulating self-development. Junior schoolchildren learn:
- Make choices according to your abilities.
- Set goals and make decisions necessary to achieve them.
- Look for a way out of difficult and unusual situations.
- Control yourself and your actions.
- Adequately assess your abilities and actions, adjust your work based on shortcomings and situations of success.
- Communicate, find a common language, coordinate your actions with others.
The innovation also lies in the fact that the number of group and individual forms of work in the classroom has increased, the authoritarian style of communication between schoolchildren and teachers is gradually transformed into fruitful cooperation.
Stages of a lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard in primary school
The modern education system does not put the main task of mechanical acquisition of knowledge in a subject, but the formation of educational actions that will help schoolchildren “teach how to learn.” Students must be able to regulate their educational activities, master the skills of self-control and self-esteem. The main stages of a lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard are goal setting, updated productive activity and summing up (reflection). It is important to understand that the implementation goals of the lesson stages according to the Federal State Educational Standard depends on the pedagogical skill of the teacher, the level of his responsibility and the quality of preparation for the lesson. In addition to the three main stages, a modern lesson has many intermediate ones, which involve eleven sequential structural elements, each of which is aimed at increasing the efficiency of the educational process at school.
| Lesson steps | Student Actions | Teacher's actions |
| Motivational | Positive emotional attitude towards studying, creating a favorable working atmosphere | Motivation for fruitful work |
| Updating knowledge | Mutual and self-examination, completing assignments on the topic of the material covered, receiving an assignment, the solution of which goes beyond the boundaries of knowledge | Advisory assistance |
| Goal setting | In interaction with the teacher, the problem and the reasons for the difficulty that have arisen are determined, the topic and purpose of the lesson are formulated | Helps schoolchildren understand the boundaries of knowledge and ignorance |
| Finding solutions to the problem | Planning ways out of difficulties, actions to lesson plan according to the Federal State Educational Standard or sample, group and individual practical work | Advisory assistance |
| Solving the problem | Trying to complete a practical task that previously seemed impossible | Advisory assistance |
| Correction | Voice difficulties and check the correctness of the practical task. | Advises, helps, consults |
| Independent work | Completing tasks based on acquired knowledge, self-checking using a sample | Advisory assistance |
| Systematization of knowledge | Establishing interdisciplinary connections, relationships between new materials and what has already been studied, | Directs group work, advises |
| Explanation of homework | Students should be able to complete tasks of varying difficulty levels, | Offers a task to choose from according to difficulty levels, explains the essence of the homework |
| Assessment | Students perform peer and self-assessment, on the basis of which the teacher assigns grades | Consults, assigns and explains assessments |
| Reflection | Students determine the subject content of the lesson, repeat the topic and goals of the lesson, analyzing how they were achieved | Answers student questions |
First stage. Goal setting
Before the introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard, this stage was of key importance, but today it has not lost its importance, although it is viewed in a different light. From now on, it is not the teacher who voices the purpose of the lesson, but creates conditions in which schoolchildren independently understand the essence of the educational task and its importance. Otherwise, motivation and focus of work are lost. Having identified the goal of the work independently, the student will demonstrate the desire to learn, find and prove.
The stage of goal setting runs through the entire lesson, so it needs to be approached with special responsibility, which is often neglected by teachers. You should not think that it is enough to overcome this part in order to move on to the rest; on the contrary, at the beginning of the lesson, it is important to motivate students for further work, to set a course according to which cognitive activity and assessment of knowledge acquisition will take place. The result directly depends on the goal, and for it to be effective, the teacher should carefully analyze the means and techniques of motivating students.
- Most often, the teacher voices the topic of the lesson, inviting students to formulate its goal using supporting verbs (consolidate, compare, generalize, find out, study, prove, analyze).
- Another option is to work on the concept. The teacher explains the meaning of each word of the topic separately, inviting the children to formulate the goals of the work based on the information received.
- Conversations focused on generalizing and concretizing a new topic. During the dialogue, the teacher allows the children to realize their incompetence in relation to the new educational material, which does not allow them to conduct conversations. Schoolchildren realize the need for research activities, thus voicing the goals of the lesson.
Second stage. Productive activity
At the main stage, attention is paid to the independent work of students, which allows them to gain knowledge through personal activities. The teacher plays the role of a mentor: he manages and controls the work of students. Students on this stage of the lesson on the Federal State Educational Standard in primary school go from ignorance to knowledge, acquire new skills and abilities, a willingness to expand their knowledge base, and isolate useful and interesting information from the general information flow.
Schoolchildren must not only gain new knowledge, but also acquire the habit of work and independent cognitive activity, which takes place in groups, individually or frontally. Independent work can be:
- According to the model - which improves the memorization of the algorithm of actions in each specific situation.
- According to the reconstructive-variative type - it is based on existing knowledge, stimulating the search for solutions to new problems.
- Heuristic - children look for a solution to a task outside of the model they are familiar with.
- Creative - schoolchildren are in a continuous search for information, improving their skills and knowledge.
Third stage. Reflection
Reflective skills - students’ understanding of the reasons for their failure or success. At this stage, the role of the teacher is especially important, since the concept of luck or bad luck is not applicable in school practice, therefore, an adult must support children even in the case of minor improvements and successes. Reflection is a stage of a modern lesson designed to stimulate children's creativity and activity, conscious internal reflection, an integral condition for the formation of a developmental environment.
Keep this for yourself so you don't lose it:
Articles in the electronic journal “Handbook for Deputy School Principals” will help you learn more about organizing analysis and self-analysis of a training session in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard.
- A template according to which teachers will prepare self-analysis of lessons for your control (professional competencies)- Identify meta-subject and personal UUD: lesson analysis sheet (quality of education)
At the reflection stage, children conduct self-analysis, assessing the results of learning activities. Systematic reflection develops the skill of self-control, self-esteem and self-regulation, the habit of comprehending problems and events. But only during the joint work of the student and the teacher is it possible to achieve the goals of effective assessment of educational activities.
Reflection can be at the beginning or at the end of the lesson:
- Mood reflection - used to establish emotional contact with children and create a psychologically favorable atmosphere. Teachers use cards with images of emoticons, pictures of the sun and clouds, various sad and cheerful animals.
- Reflection on activity - schoolchildren reflect on ways and techniques of work, real achievements, success and failures during class. This type of self-assessment is most often used at the end of the lesson.
Stages of a lesson in discovering new knowledge according to the Federal State Educational Standard
Among all types of lessons, a special place is occupied by the lesson of discovering new knowledge, which should be carried out according to an established scheme. Stages of a Russian language lesson, mathematics according to the Federal State Educational Standard, if the classes are devoted to the discovery of new knowledge, remain unchanged. A training session of this type is subject to activity and content goals:
- Teaches children new ways to gain knowledge.
- Introduces students to new terms, concepts and principles of action, forming them into a single conceptual and effective system.
- Expands the knowledge base to include new knowledge and skills.
| Motivation for cognitive activity | At the motivational stage, the teacher stimulates children’s internal readiness for learning, interest in acquiring new skills and meeting established standards. To do this, he updates the requirements for students, forms the thematic framework of the work and creates conditions for the emergence of the need for cognitive activity. |
| Updating knowledge and trial task |
On this stage of the lesson of new knowledge according to the Federal State Educational Standard The teacher prepares children to recognize the need to develop a new model of action. To do this, he offers schoolchildren:
|
| Determining the problem and its cause |
It is important for students to realize their lack of knowledge, skills or abilities, for which the teacher offers them:
|
| Project activity and problem solving | It is necessary to formulate problems on the basis of which to develop a solution algorithm. To do this, a learning action is determined that will eliminate the cause of the difficulties, the topic of the lesson is agreed upon, an algorithm for obtaining missing knowledge is determined (methods of addition and clarification are used), and means of knowledge formation are determined (formulas, concepts, algorithms or models). |
| Implementation of the created model |
Schoolchildren must create a new algorithm of actions and learn to apply it to solve problems that caused them difficulties. To do this, during the lesson they:
|
| Primary consolidation of material with voicing of information | For students to learn new method solving problems, primary consolidation is necessary. To do this, they say their actions out loud, justifying them, and then solve several similar problems to consolidate the skill. |
| Independent activity with mandatory self-control | Teenagers independently check and evaluate their mastery of acquired skills and information. They check the solution according to the sample, noting the results, noting the absence of difficulties that previously arose, and successfully completing similar tasks. If no difficulties arise during the development of new knowledge, students are asked to complete creative tasks and test them independently. |
| Incorporating new knowledge into the educational process |
To consolidate the acquired skills and knowledge, prepare the class for the study of the following topics and sections, it is necessary to successfully apply the developed model of action in practice. Teachers offer:
If during the implementation of the lesson it was not possible to achieve a situation of success, self-control and independent work are repeated in the class. |
| Reflection |
Teenagers must recognize and overcome the difficulties that have arisen and successfully complete independent work:
|
Stages of conducting a lesson of general methodological orientation according to the Federal State Educational Standard
General methodological training sessions fall into the category of combined ones, aimed at developing an understanding of the relationship between techniques, skills and knowledge. Schoolchildren develop norms of self-control and their own principles for assessing the structure of educational activity and its reflection. General methodological classes are classified as meta-subject classes, since they are conducted on extracurricular activities or class hour. Stages of conducting a lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard, a sample of which can be downloaded on our resource, comes down to five main components.
| Lesson stage | Teacher's actions | Student Actions |
| Motivation | Stimulates cognitive activity, leads schoolchildren to independently determine the topic, goals and objectives of the lesson | Formulate goals and objectives, draw conclusions |
| Updating and defining individual difficulties | Updates information resources and existing skills and knowledge, analyzes previous work. | Choose the maximum effective way organizing the learning space, dividing into groups, distributing responsibilities to obtain new knowledge, working with resources, interacting with the teacher. |
| Consolidation of knowledge | Organizes work in groups, pairs or individually, provides advisory assistance | Interact with classmates, establish partnerships during analysis, discussion, and structuring information |
| Putting what you've learned into context common system knowledge | Initiates discussion with building cause-and-effect relationships, according to stages of the lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard | They express their opinions, oppose their classmates, make predictions, evaluate the relationship between new things and what they have already learned. |
| Reflection | Organizes a discussion of the results of collective and individual work, the degree of implementation of set goals | Consciously evaluate work and the correctness of actions, draw reasoned conclusions, communicate, and come to a common opinion regarding the effectiveness of work in the classroom |
Stages of a reflection lesson
A reflection lesson is conducted to find and overcome difficulties in educational algorithms. Schoolchildren perform exercises during classes, forming mechanisms for assessing and correcting their own activities. It is important not only to identify the mistakes made and correct them, but also to master the correction algorithm in order to achieve impeccable performance of standard tasks in the future. As a result of implementation new stages of the lesson according to the Federal State Educational Standard the quality of mastering educational material improves, children easily transfer the experience accumulated in reflection lessons to classes in other disciplines.
A reflective learning session fulfills content-based and activity-based goals, developing correctional-control type reflection skills and the ability to independently find and eliminate the cause of difficulties, as well as the ability to correct and consolidate proven methods of action used to overcome difficulties.
Classes of this type are easier for teachers because, despite the need for careful preparation, they do not require a transition to a new method of work. The lesson is conducted in nine stages:
- Motivation for correctional activities - a readiness to fulfill regulatory requirements is developed, for which conditions are created for the emergence of an internal need for activity (“I want”), requirements are updated (“I must”) and the framework for correctional work is established (“I can”).
- Actualization and trial educational action - preparation for finding out the causes of difficulties, for which they stimulate thought processes, repeat the methods of action necessary for reflexive analysis, organize independent work according to the example of the method of action, followed by self-testing and recording the results.
- Localization of individual difficulties - the moment of difficulties is determined, for which an error correction algorithm is selected, and then the methods of action that caused the difficulties are determined. Teenagers who have not made mistakes check the solution step by step using the model to eliminate the situation of accidentally selecting the correct answer, or perform a creative task.
- Goal setting and project development - the goals of correctional activities, means and methods of their implementation are determined, for which samples and work standards are determined.
- The implementation of the developed project is a meaningful correction of one’s own mistakes with the development of the skill to use the correct methods of action, for which students independently correct errors using the chosen means, and if difficulties arise, they use a self-test standard.
- Generalization of difficulties - consolidation of actions that cause difficulties, for which typical difficulties are discussed in class, methods of action are formulated (it is important that children who have made mistakes understand and speak out the correct methods of action).
- Independent work with self-test - understanding the method of action that caused difficulties, self-test and individual assessment of the goal and its degree of implementation. Having made mistakes, students do independent work similar to the one that caused difficulties, check them against a sample and remember the results.
- Inclusion in the knowledge system and repetition - using tested methods of action in practice, consolidating what was previously learned, repetition and preparation for the next topics, for which children complete tasks to motivate them to study the following sections, do tasks that connect already familiar methods of action with new ones. If difficulties arise, the previous step is repeated.
- Reflection - understanding the correct choice of method for eliminating difficulties, self-assessment of correctional work, for which schoolchildren evaluate work in class, name the goals of the next lessons, methods of action that provoked difficulties.
Stages of a lesson on developmental control
Developmental control classes involve writing tests followed by reflective analysis. Federal State Educational Standard there are two stage of the lesson on developmental control, which are carried out upon completion of the study of voluminous topics: in the first lesson, students write a test, and in the second (the test time should not exceed one or two days) they conduct criterion-based assessment and reflective analysis of mistakes made.
The classes focus on defining assessment criteria to establish compliance with the control structure and comparison with the mark. Depending on the form of organization of the lesson, control lessons are distinguished:
- self-control - the student receives a standard version, which he compares with his own, evaluating according to established criteria;
- mutual control - another student becomes a model for testing; the ability to fairly evaluate a classmate’s work and analyze mistakes is also tested;
- pedagogical control - the teacher becomes the holder of the sample, and assessment is carried out through reflection and correlation with established criteria.
Lesson 1 (test):
- Self-determination and motivation for control and correctional activities;
- Updating - awareness of the need to conduct control with individual writing test work, subsequent self-assessment and comparison of work with a sample.
Lesson II (activity analysis)
The second lesson is held after the teacher checks the tests and is devoted to working on mistakes. Stages lesson of developmental control on the new Federal State Educational Standards:
- Motivation.
- Updating the work.
- Localization of individual difficulties - the correctness of self-tests by students is assessed, followed by drawing up a model for correcting errors and determining the location of difficulties. Those who completed the test without errors consult classmates or do creative tasks.
- Project development - formulating the purpose of working on errors, choosing the means and method of carrying out correction work.
- Project implementation is meaningful work on errors and their subsequent correction using the chosen method or using the proposed sample. Students come up with or choose from the proposed exercises for selected methods of action that caused difficulties in solving. Schoolchildren who completed the test without errors consult their classmates or do creative tasks.
- Generalization of difficulties - correct methods of action are reinforced in practice, for which typical errors are discussed and solution algorithms are spelled out.
- Independent work with self-test - interiorization of the algorithm followed by assimilation and individual reflection, for which tasks similar to those given on the test are solved, self-test is carried out according to the standard. Those who did not make mistakes in the test do a self-test of creative level exercises based on the model.
- Creative level tasks - solve tasks to prepare for studying the next thematic blocks, and if they fail at the previous stage, return to completing another option.
- Reflection - self-assessment, awareness of the effectiveness of working on mistakes and the chosen methods of overcoming difficulties, indicate further goals.
Administrative control lessons, which are often conducted in pedagogical practice, do not realize activity goals. Developmental control presupposes the presence of a controlled option, a justified sample and an agreed upon mechanism for comparing work with the sample.
The formula for lesson effectiveness includes two components: thorough preparation and skill in delivery. Poorly planned, poorly thought out, hastily designed and not matched to learner capabilities
the lesson cannot be of high quality. Preparation of a lesson is the development of a set of measures, the choice of such an organization of the educational process that, in given specific conditions, ensures the highest final result.
In preparing a teacher for a lesson, there are three stages: diagnostics, forecasting, design (planning). In this case, it is assumed that the teacher knows the factual material well and is fluent in his subject. He maintains and expands his own so-called thematic folders or workbooks, where he enters latest information that appeared in the area of the subject he taught, problematic questions and assignments, test materials, etc. To successfully prepare a lesson, we emphasize once again, it is important that the teacher does not have problems with actual assignments, so that he confidently masters the educational material.
Preparatory work comes down to “adapting” educational information to the capabilities of the class, assessing and choosing a scheme for organizing cognitive work and collective cooperation that will give the maximum effect. To choose the optimal lesson plan, you need to go through the canonical path of calculating the training session. It is based on an algorithm for preparing a lesson, the sequential implementation of the steps of which ensures that all important factors and circumstances are taken into account, the effectiveness of the future lesson depends on them.
The implementation of the algorithm begins with diagnosing specific conditions. Diagnostics(it has already been discussed in connection with the design of educational work) is to “clarify” all the circumstances of the lesson: the capabilities of students, the motives of their activities and behavior, requests and inclinations, interests and abilities, the required level of training, the nature of the educational material, its features and practical significance, lesson structure, - as well as in a careful analysis of all the time spent in the educational process - on repetition (updating) of basic knowledge, assimilation of new information, consolidation and systematization, control and correction of knowledge and skills. This stage ends with the receipt of a diagnostic lesson card, which clearly shows the effect of the factors that determine the effectiveness of the lesson. The greatest quality is expected when the factors are in the zone of optimal conditions.
Forecasting is aimed at assessing various options for conducting a future lesson and selecting the optimal one according to the accepted criterion. Modern forecasting technology makes it possible to derive a quantitative indicator of the effectiveness of a lesson in the following way. The volume of knowledge (skills), the formation of which is the goal of the lesson, is taken as 100%. The influence of interfering factors naturally reduces this ideal indicator. The amount of loss (it is determined using a special method) is subtracted from the ideal result and determines the real indicator of the effectiveness of the lesson according to the scheme conceived by the teacher. If the indicator satisfies the teacher, he proceeds to the final stage of lesson preparation - planning, and if not, the teacher is forced to look for a more advanced organization scheme, manipulating those factors whose influence he can change.
Design(planning) is the final stage of lesson preparation, and it ends with the creation of a control program cognitive activity students. A management program is a short and specific, arbitrarily compiled document in which the teacher records important aspects of process management for him: who and when to ask, where to introduce the problem, how to proceed to the next stage of the lesson, what scheme to rebuild the process in case of pre-foreseen difficulties and etc. The control program differs from the traditional lesson plan in its clear, specific definition of control actions.
Beginning teachers should write detailed lesson plans. This requirement is derived from practice: no one has yet managed to become a master without understanding in all the details the organization of the upcoming lesson. Only when most of the structures become familiar can you move on to abbreviated entries, gradually reducing the scope of the plan, turning it into a specific program of action.
The beginning teacher’s plan should reflect the following points:
Date of the lesson and its number according to the thematic plan;
The name of the topic of the lesson and the class in which it is taught;
Goals and objectives of education, upbringing, development of schoolchildren;
The structure of the lesson, indicating the sequence of its stages and the approximate distribution of time for these stages;
Methods and techniques of the teacher’s work in each part of the lesson;
Training equipment necessary for conducting the lesson;